Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices of Community Pharmacy Personnel in Tuberculosis Detection, Drug Monitoring and Education
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.38040/js.v17i03.1276Abstract
Introduction: Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease that remains a public health problem in Indonesia, including in Lamongan Regency. The role of community pharmacy worker (pharmacists and pharmacy technicians), is crucial in early detection, treatment monitoring, and TB patient education. This study aims to determine the level of knowledge, attitudes, and practices of community pharmacy workers regarding TB management.
Methods: This study used a descriptive design with a cross-sectional approach, conducted from January to May 2025. The sampling technique used simple random sampling, with 75 respondents from pharmacy worker in Lamongan. Data were collected using a KAP questionnaire adapted from previous studies and tested for validity and reliability.
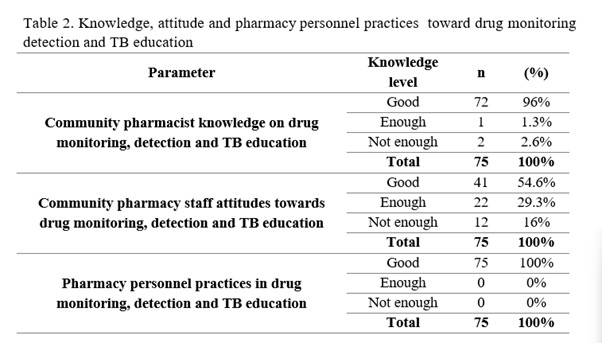
Results: Knowledge research shows that of the total 75 respondents, as many as 72 people (96%) are in the good knowledge category, while only 1 person (1.3%) has sufficient knowledge, and 2 people (2.6%) are included in the poor knowledge category, most respondents have a good level of knowledge about TB. In the results of the attitude study, the level of knowledge is good (54.6%), respondents with a sufficient level of attitude are 29.3%, and 16% are in the poor category. And the results of practice (100%) have a good level of knowledge in the practice of detection, drug monitoring, and education of TB patients. Factors that influence include educational background, work experience, and training related to TB.
Conclusion: While pharmacists’ knowledge and practice are high, sustained and continuous training is crucial to maintain performance and reinforce their contribution to TB control
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Citation Check
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Andy Ilham, Devi Ristian Ristian, Sri Bintang Sahara Mahaputra Kusuma Negara

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions.
- The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY).










